Master of Civil Engineering (Online)
Elevate your Civil Engineering career with a Masters Degree – Designed for busy professionals Talk to an AdvisorApply NowMaster of Civil Engineering (Online)
Elevate your Civil Engineering career with a Masters Degree – Designed for busy professionals Talk to an AdvisorApply NowFACULTY OF ENGINEERING AND DESIGN
MCivilEng
Whether you’re a seasoned civil engineer seeking leadership opportunities or a professional from a related field like architecture or construction management, the Master of Civil Engineering will help you gain the advanced knowledge, skills, and professional credibility needed to lead engineering teams, manage complex projects, and navigate the dynamic world of civil engineering.
Entry Requirements
A Bachelor of Engineering,
or a Bachelor of Engineering (Honours),
or a relevant Bachelor with relevant work experience
or a relevant Bachelor with a relevant Postgraduate Diploma
Please see the regulations for more details.
*Alternative pathways are available for those who do not meet the above requirements.
Duration
2 years (part-time)
1 Year (full-time)
Next Start Dates
2025
Semester 1:
3 March (Applications close 17 February)
Semester 2:
21 July (Applications close 7 July)
Full Programme Fees
$11,440.80
Why is this programme right for you?
The Master of Civil Engineering (MCivilEng) opens doors to leadership positions and significantly increases your earning potential in the competitive engineering sector. With this advanced qualification, you can differentiate yourself from your peers and access higher-paying roles that align with your career aspirations.
The curriculum is designed to ensure you acquire the most up-to-date knowledge and skills. Deepen your understanding of cutting-edge civil engineering practices, master critical thinking and problem-solving, and develop the specialised expertise necessary to excel as a civil engineer in New Zealand or overseas.
A 120-point Postgraduate Diploma in Civil Engineering and a 60-point Postgraduate Certificate in Civil Engineering are also available as qualifications for students seeking shorter qualifications.
Programme Brochure
What are the key benefits?
1. Unlock Leadership and Management Opportunities:
Gain the advanced knowledge, skills, and professional credibility needed to lead engineering teams, manage complex projects, and navigate the dynamic world of civil engineering.
2. Increase Your Salary Potential:
A Masters degree opens doors to leadership positions and significantly increases your earning potential in the competitive engineering sector. With this advanced qualification, you can differentiate yourself from your peers and access higher-paying roles that align with your career aspirations.
3. Master Cutting-Edge Skills:
Benefit from the expertise of leading academics and industry professionals. The curriculum is designed to ensure you acquire the most up-to-date knowledge and skills. Deepen your understanding of cutting-edge civil engineering practices, master critical thinking and problem-solving, and develop the specialised expertise necessary to excel as a civil engineer in New Zealand or overseas.
4. Connect with Industry Leaders:
Network and collaborate with experienced professionals through interactive, live sessions led by expert academics. Gain valuable insights from fellow professionals and build relationships that can benefit your career.
5. Address Real-World Engineering Challenges:
Explore real engineering challenges faced by New Zealand companies. Apply your learning to develop complex engineering problems and enhance your decision-making skills.
6. Earn a Globally Recognised Qualification:
The University of Auckland is ranked 1st in New Zealand and 46th in the world for Engineering, ensuring that your masters degree is respected and valued both domestically and internationally.
Programme Structure
The Master in Civil Engineering is a 120-point programme consisting of 7 or 8 courses. Each course runs over a 12-week Semester, enabling you to complete this programme in 2 years part-time, or 1 year full-time.
In this programme, you will complete either 6 taught courses and one 30-point research project course, or 8 taught courses. If you elect to take the 30-point research course (CIVIL 788A/B), the MCivilEng will be eligible for being awarded with Honours, and it will also provide you with the option to potentially progress to PhD study in the future.
The programme is divided into the following course groups: Core courses, designated courses, and elective courses. You will be required to take all the core and designated courses, but you will have an option to select which elective courses you wish to take.
Please note that the University of Auckland Online courses are scheduled on rotation, and not all elective options will be available each semester. Where there are elective options, we will enquire with you on your preferred course selections prior to proceeding with your course enrolments.
ENVENG 702 (Core) - Engineering Decision Making in Aotearoa
Advanced systems engineering based decision making; complex problem framing including ontology analysis; cultural opportunity mapping; absolute sustainability analysis; risk threshold determination; temporal cumulative effects; and effective consultation. Independent research is undertaken to solve a complex engineering decision making problem.
ENGGEN 730 (Core) - Management Skills for Project Professionals
Core theories and their implications for the art and practice of project management in organisations.
CIVIL 702 (Designated) - Design of Earthquake Resistant Foundations
Observed behaviour of foundations during earthquakes. Site investigation and laboratory testing to estimate values for required soil parameters. Earthquake induced foundation actions. Shallow and deep foundations subject to earthquake excitation. Soil-foundation-structure-interaction. Force-based and displacement-based design. Earthquake induced earth pressures on stiff retaining structures. An independent foundation design project is required.
CIVIL 715 (Designated) - Advanced Structural Concrete
Design and detailing of prestressed and precast concrete components. Advanced mechanics of reinforced concrete members subject to axial, flexure, shear, and torsion actions. Design of state-of-art low-damage concrete structural systems. Includes an independent concrete design project and an independent research project on past failures of concrete structures.
ENGGEN 742 (Designated) - Project Management
Planning, organisation and control of projects in ordered environments. Application of project management principles, concepts, disciplines, tools, techniques and processes to the typical project lifecycle. Studies in the knowledge areas/domains defined by the Project Management Institute (PMI). Development of a range of skills, tools and techniques to become an effective project manager.
ENVENG 746 (Designated) - Surface Water Quality Modelling
Advanced specialist topics in modelling of lakes and rivers. Specific topics covered include response to different loadings applied to surface water systems, and modelling of organic matter, dissolved oxygen consumption, eutrophication, and toxic substances. The core taught skills are extended by an individual project in which independent research is undertaken to solve a challenging surface water quality engineering problem.
ENGGEN 737 (Elective) - Engineering Risk Management
The theory and practice of risk management, providing a comprehensive approach to identify, analyse, and treat risks inherent in engineering projects. Critical analysis and synthesis of risk management frameworks to deliver outcomes in scenarios of uncertainty and to communicate plans at a professional level. An independent project is undertaken in which students apply risk management theories to engineering projects.
ENGGEN 743 (Elective) - Applied Creative Thinking
Application of inventive problem solving and creative thinking to formulate novel engineering solutions. Theories, tools and techniques to assist with generating innovative ideas are reviewed and evaluated. Techniques for improving the creativity of teams are critiqued. Develops skills in the facilitation and leadership of virtual and face-to-face workshops to help teams solve complex problems. Practical application of the concepts are synthesised to solve case study scenarios, live problems from industry, and students’ individual problem scenarios.
CIVIL 788A/B (Elective) - Project Y
Students are required to submit a report on a topic assigned by the appropriate Head of Department.
Master of Civil Engineering – Enquire Now
Experimenting with programming in the browser
How to Learn the Basics of Programming? Getting started with programming can be a daunting prospect. Reading code can seem like you're reading a foreign language. Also, there are a huge amount of resources available online - but where do you start? Today we'll be...
Educational Leadership During Challenging Times
The pandemic has pushed us to make change, to transform our practice, to relate to each other in new ways and to think differently about what it means to learn and lead and how learning and leadership happens. As leaders under these conditions we can sometimes...
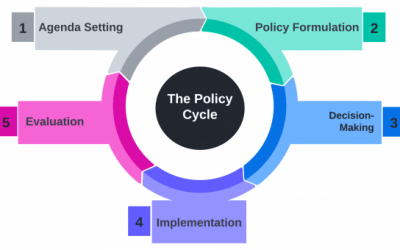
Perspectives in Public Policy – The Policy Cycle
What is Public Policy? According to Wilson (2009), public policy is what governments decide to do, or not do, and their explanations for the outcomes of those decisions in the real world. A recent example of this is the government's 2019 cash injection into the mental...